
Unlocking the Mystery of Gluten & How it Stresses Your Body (Infographic)
- Home
- Leaky Gut & Food Sensitivity
- Unlocking the Mystery of Gluten & How it Stresses Your Body (Infographic)
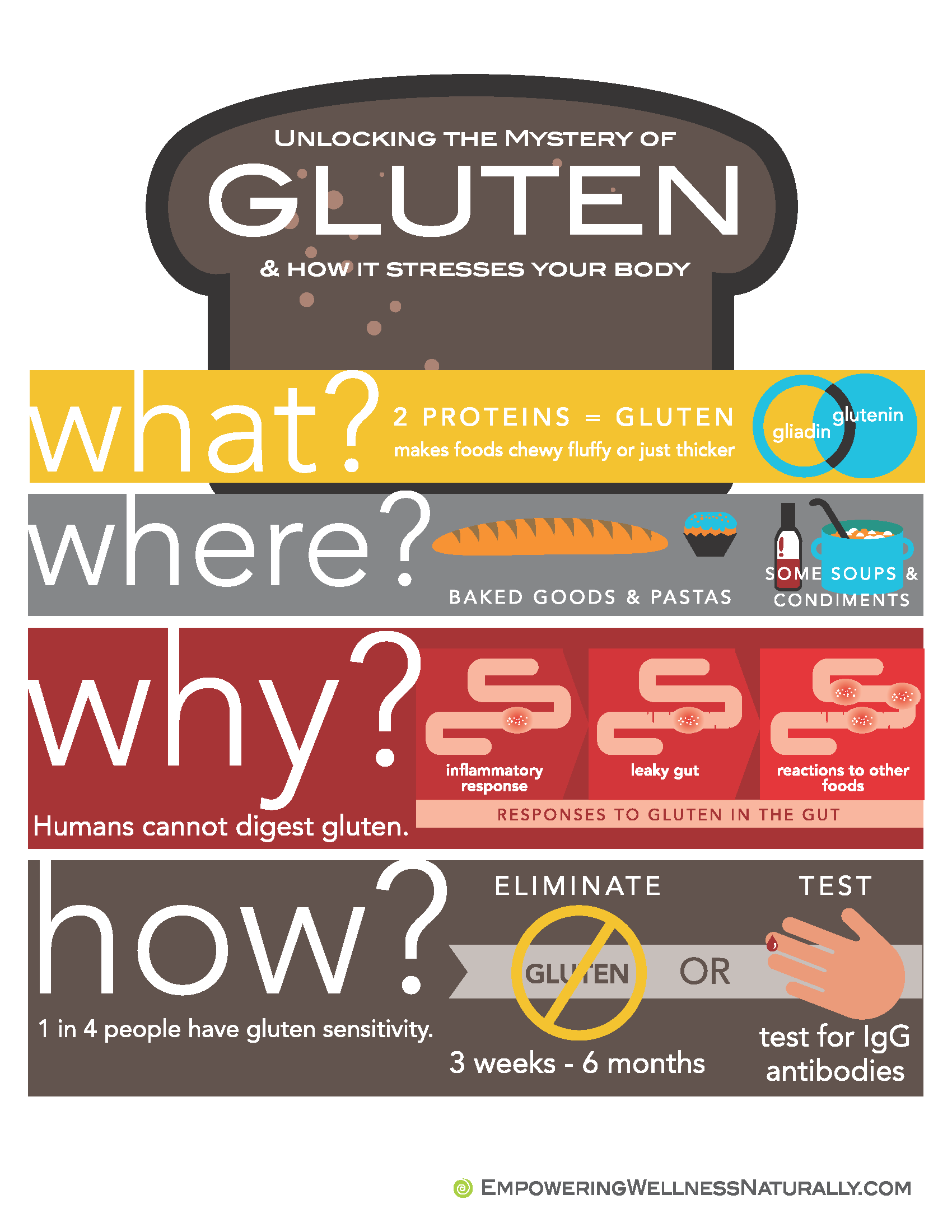
Dr. Doni Wilson, naturopathic doctor and health expert, covers the basics of gluten—what it is, where it’s hiding, and why it’s a problem for most of us.
Do you know someone who has gone gluten-free?
Odds are, you do. Gluten-free living is all the rage, but few know exactly what gluten is and how it impacts our bodies.
Let’s clear up the confusion here—it’s quite simple, actually. After years of research and observing thousands of patients that feel better without gluten (not to mention myself, too!), I am happy to shed light on the mystery of gluten and explain how gluten can cause stress in your body.
Why is Gluten Unhealthy?
The simple truth is that humans cannot digest gluten. We can consume foods that we can’t digest—we also cannot digest fiber and beans, for example. In small quantities, it is usually not an issue.
The problem comes into play when we consume large amounts of gluten (in every meal, for example) and especially if we have a genetic tendency to react to gluten. Here’s what happens: undigested proteins from gluten (also known as gliadin and gluten in) get noticed by the immune system in our gut, triggering an inflammatory response that can spread throughout the body.
What are the Negative Health Consequences of Gluten?
Gluten causes leaky gut (called intestinal permeability in scientific terms), an issue in which the cells lining the intestines – and the spaces between them – are damaged, allowing undigested food to leak through (gluten, as well as other food) and trigger inflammatory responses while decreasing absorption of nutrients.
Leaky gut has been associated with such chronic health issues as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, liver disease, neurological issues (like migraines, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s), autoimmune conditions (such as Hashimoto’s, rheumatoid arthritis, MS, and others), women’s health issues (including PCOS), and cancer.
Then, there’s celiac disease, which is an autoimmune disease in which further damage to the intestines due to immune responses to gluten can cause severe and life threatening health issues. It is estimated that 1 in 133 people have developed celiac disease already – that’s over 2 million people in the U.S – and most of them have no idea.
Even if you don’t have celiac disease, it is thought that at least 1 in 4 people develop what is now known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS). NCGS is associated with a number of health issues varying from fatigue and IBS to depression, anxiety, migraines and PMS. The effective treatment for both celiac disease and NCGS is the avoidance of gluten.
How Does Gluten Cause Stress on the Body?
Once gluten causes leaky gut and the immune system in the intestines starts reacting to gluten, it is exponentially more likely that the immune system will start reacting to other foods—most often dairy proteins (casein and whey), eggs, potato, soy, and other grains (rice, millet, and corn)—because they too will leak through the intestinal lining.
At this point, a person is often hit by digestive symptoms no matter what they eat, and potentially experiences fatigue, sleep issues, mood changes, skin rashes, frequent infections, thyroid issues, and in some cases, autoimmunity.
It is important to keep in mind, however, that gluten and leaky gut does NOT always cause digestive issues. In fact, studies show that at least 50% of people do not have digestive issues when they react to gluten, and instead are more likely to experience neurological symptoms, such as depression, anxiety, headaches, and insomnia.
What is Gluten?
Gluten is the protein aspect of certain grains, including wheat, barley, rye and spelt.
When you eat these grains, or foods containing them, you are eating gluten.
The most common foods containing gluten are bread, pasta, pizza crust, bagels, cookies, and pastries. So you can see, it is quite easy to be exposed to gluten everyday—and even every meal.
Where is Gluten Hiding?
In addition to the common places we find gluten, it can also be found hidden in many other foods because it helps to thicken liquids and allows things to stick together. It can also create a chewy and/or fluffy texture. This is why it is used in soups (even miso soup), gravy, dressings, sauces, pastries, cookies, cakes, soufflés, pasta, cereals, and breads.
Gluten also hides in products you wouldn’t think of based on their chewiness. Soy sauce, for example, contains gluten – so be sure to choose the gluten-free alternative called tamari sauce. Sometimes, other condiments, like mustard, ketchup, and BBQ sauce, may also contain gluten. Then there are flavored chips and crackers. Even corn chips, if they are spicy or flavored in any way, may well include flour and/or wheat in their ingredients lists. The same goes for anything seasoned such as spice mixes (taco mix, for example) or anything containing modified food starch (even chewing gum).
In 2013 the FDA defined “gluten-free” as containing less than 20 ppm of gluten. Companies had until August of 2014 to comply with the rule. So look for the words “gluten-free” on labels, and, I would say, also review the ingredients of products you are thinking of purchasing to make sure all the ingredients are, in fact, free of gluten.
Identifying a Gluten Intolerance
As mentioned before, 1 in 4 people have a gluten sensitivity—so it’s quite possible, if not likely, that you have one.
Some indications include tiredness, anxiety, depressed mood, insomnia, bloating, IBS, eczema, allergies, sinusitis, and low thyroid function. Even hormone imbalances—such as PMS, PCOS, and unexplained infertility—have been tied to gluten intolerance.
Currently research indicates that the best way to determine whether you have gluten sensitivity is to remove gluten from your diet for at least three weeks (however, in some cases, it could require six months of elimination) and then reintroduce gluten to determine whether symptoms occur or return.
Another option is to test for IgG and IgA antibodies to gluten, which can be done with as little as a finger prick, although most practitioners are not offering this panel or may not be familiar with the relevance of the results. You can order a test kit here to do at home and find out if your immune system is reacting to gluten and 95 other foods.
Conclusion: Are Gluten-Free Diets a Fad?
While many people question whether avoiding gluten is a fad, I would say that it is actually a much-overdue awareness for the trouble that gluten causes for our bodies. The exposure to gluten in the human diet, and more specifically, the American diet, has increased in the past 50 years, and it is only recently that research and practitioners have realized the number of cases that could benefit from the avoidance of gluten in the diet. Previously it could take decades for patients to find out that gluten was an underlying cause of their distress.
I encourage you to find out for yourself whether gluten is contributing to your health issues and then make the necessary diet changes to eliminate gluten from your diet. It could make all the difference in your health.
If you wish to learn more about a gluten-free lifestyle:
- Please read (and share!) my Basics of Gluten posts: http://bit.ly/gluten-basics
- Or read my book, The Stress Remedy: http://thestressremedy.com (which includes 150+ gluten-free recipes!)

To download a printable version of this infographic, click here.
—
This article by Dr. Doni Wilson was orignally published on Inspiyr.com.
Share this Post:
Dr. Doni Wilson's Team
14 Day Detox Program
Take the Stress Type Quiz
Dr. Doni Social Media
Popular Posts


The 5 Burnout Types

Healing HPV Holistically: Dr. Doni on the Inspire Health by Jen Podcast

Recent Podcasts
Signup to receive our weekly newsletter with all the latest news, podcasts and special offers
New Book - Order Today!

SIMPLE PRACTICES for SHIFTING FROM YOUR STATE of STRESS to YOUR FLOW and FREEDOM
MASTER YOUR STRESS
RESET YOUR HEALTH
Order Now! Related Posts

What is making you susceptible to HPV?
I have been working with women who had abnormal cells on their cervix and/or vaginally, caused by HPV for over 20 years now. And while

The 5 Burnout Types
Did you know there are 5 burnout types? They are based on your Stress Type®, which is how your adrenal function has been affected by

Healing HPV Holistically: Dr. Doni on the Inspire Health by Jen Podcast
Dr. Doni was interviewed by Jen Ciszewski on the Inspire Health by Jen Podcast, talking about how to heal away HPV from your body for good.

Stress and Trauma: The Science Behind It, How It Shows Up and How to Heal: Dr. Doni on The Burn Fat and FEAST Podcast
Dr. Doni was interviewed by Sarah B. Thomas on the Burn Fat and FEAST Podcast, talking about the impact of stress and trauma on our health and what to do to recover from them.














